Immersive audio sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This technology has evolved tremendously, transforming the way we perceive sound, whether in entertainment, gaming, or even educational settings. By creating a three-dimensional soundscape that envelops the listener, immersive audio enhances experiences and makes them feel more lifelike.
From its early beginnings with basic stereo systems that lacked depth to the sophisticated multi-dimensional sound technologies we have today, immersive audio showcases a remarkable journey. It’s not just about listening anymore; it’s about being part of the sound environment, where every subtle shift can create an emotional impact. As we delve deeper into this fascinating realm, we will explore its evolution, importance, and future potential.
The Evolution of Immersive Audio Technologies
Immersive audio technologies have dramatically transformed the way we experience sound, moving from basic stereo systems to complex surround sound and spatial audio formats. This evolution has not only enhanced the quality of sound but has also enriched our listening experiences across various platforms, from cinema to virtual reality.
The journey of audio technology began with simple monophonic systems that provided a single channel of sound. These early systems lacked the depth and spatial awareness that modern listeners expect. As technology advanced, stereo sound emerged in the mid-20th century, introducing two channels of audio that created a sense of directionality. However, stereo sound still faced limitations in creating an enveloping audio experience, primarily because it relied heavily on speaker placement and spatial separation.
Key milestones in the development of immersive audio technology include the introduction of surround sound systems in cinemas during the 1970s. Formats such as Dolby Stereo used four channels to create a more immersive experience, allowing audiences to feel as if they were part of the action on screen. The late 1990s saw the rise of 5.1 surround sound, which added a dedicated low-frequency effects channel, enhancing the audio landscape for home theaters. This technology paved the way for more sophisticated systems that could replicate a three-dimensional sound environment.
Recently, advancements in audio processing and playback technologies have led to the development of object-based audio formats like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X. These systems allow sound designers to place audio objects in a three-dimensional space rather than confining them to specific channels. This gives listeners the sensation of sound coming from above, below, and all around, creating a truly immersive experience. With the rise of streaming services and advancements in headphone technology, even personal listening experiences have become more dynamic, with binaural audio techniques that simulate how we naturally hear sounds.
In summary, immersive audio technologies have evolved from basic monophonic systems to sophisticated multi-dimensional audio experiences, making significant strides in enhancing how we perceive sound in entertainment and beyond. These advancements not only reflect technological progress but also a deeper understanding of human auditory perception.
The Importance of Spatial Awareness in Immersive Audio Experiences
Spatial awareness plays a pivotal role in crafting immersive audio experiences that can transport listeners into different environments. This concept encompasses the ability of sound to create a three-dimensional space, allowing individuals to perceive the direction, distance, and movement of sounds as if they were occurring in real life. This realism is essential for various applications, including gaming, virtual reality, and film, where the goal is to enhance the user experience through auditory cues that mimic real-world scenarios.
The way sound localization impacts listener perception is significant. Sound localization refers to the ability to identify the origin of a sound in a three-dimensional space. Our brains process auditory information from two ears, analyzing differences in volume and timing to determine the direction from which a sound is coming. This capability is crucial in immersive audio experiences, as it allows listeners to feel completely enveloped by the environment being simulated. For instance, in a video game, the subtle sounds of footsteps behind a player can trigger a visceral reaction, prompting them to turn around to see what’s approaching. Similarly, in a virtual reality setting, the sound of a bird chirping from above can enhance the sensation of being in a park, adding to the overall realism of the experience.
Environments Enhanced by Spatial Awareness
Spatial awareness is particularly essential in environments where realism and immersion are paramount. The following scenarios illustrate how spatial audio significantly enhances the listener’s experience:
- Gaming: In video games, spatial audio elevates gameplay by providing a realistic soundscape. Players can hear sounds coming from their environment, such as the rustling of leaves or distant explosions, allowing for strategic decision-making. AAA titles like “Call of Duty” and “The Last of Us Part II” utilize advanced audio techniques to ensure that players can discern the direction and distance of in-game sounds, impacting their gameplay and overall enjoyment.
- Virtual Reality: Virtual reality applications rely heavily on spatial audio to create an immersive experience. For example, in platforms like Oculus Quest, users can engage with environments where sounds dynamically change based on their movements. The sound of water flowing from a nearby stream appears different when the user moves closer or further away, enhancing the sense of presence.
- Film and Theatre: In cinematic experiences, spatial audio draws viewers into the narrative. Techniques such as Dolby Atmos create a three-dimensional sound environment, allowing sounds to move in space around the audience. In scenes depicting a busy city, the layering of sounds can create a more profound emotional response, making viewers feel as if they are part of the story.
- Live Events and Concerts: At concerts, spatial audio technologies can enhance the performance by creating an enveloping sound experience. Acoustic engineering techniques allow sound to be strategically placed within a venue, ensuring that every audience member receives an optimal listening experience regardless of their location.
The integration of spatial awareness in these environments not only improves realism but also amplifies emotional engagement, making the audio experience resonate more deeply with the audience. By simulating how we naturally perceive sound, immersive audio technologies create a sense of presence that is increasingly sought after in various media formats.
The Impact of Immersive Audio on Various Industries
Immersive audio technology has rapidly transformed how various industries operate, enhancing both user experience and engagement. By providing a multi-dimensional sound environment, immersive audio creates a sense of presence that traditional audio formats cannot achieve. This has led to significant applications across entertainment, healthcare, and education, each benefiting uniquely from this innovative audio experience.
Applications in Entertainment and Healthcare
In the entertainment industry, immersive audio is utilized to create engaging experiences that captivate audiences. For example, virtual reality (VR) games and movies leverage spatial audio techniques to enhance storytelling, allowing users to feel as though they are part of the narrative. Notable examples include films like “Dunkirk,” which used immersive audio to evoke a sense of realism and urgency, and various VR games that provide lifelike environments through sound.
In contrast, the healthcare sector employs immersive audio primarily for therapeutic and training purposes. Sound therapy, for instance, uses tailored audio environments to help patients manage pain and anxiety. Research has shown that immersive audio can significantly reduce stress levels, leading to better outcomes in patient care. Additionally, medical training simulations utilize immersive audio to create realistic scenarios for healthcare professionals, enhancing their decision-making skills and preparedness in real-life situations.
Potential in Education and Training Environments
The potential of immersive audio in education and training is particularly promising. By creating an engaging learning environment, this technology can help facilitate more effective teaching methods. Immersive audio can enhance historical reenactments, allowing students to experience events as if they were truly present. This method not only makes learning more engaging but also improves information retention.
In professional training, immersive audio can simulate realistic workplace scenarios, providing trainees with a safe space to practice their skills. For example, flight simulators incorporate immersive audio to replicate the cockpit environment, helping pilots develop their abilities in a controlled setting. The use of immersive audio in these training applications results in deeper understanding and better preparation for real-world challenges.
“Immersive audio creates a sense of presence that enhances both the learning and therapeutic experiences across various industries.”
Techniques for Creating Immersive Audio Content
Creating immersive audio content involves a blend of innovative techniques that allow listeners to experience sound in a multidimensional space. This approach transcends traditional stereo sound, engaging the listener in a way that feels both natural and enveloping. The pursuit of creating immersive audio experiences has led to the evolution of technologies like binaural recording and ambisonics, each providing unique advantages in crafting rich audio landscapes.
Binaural Recording
Binaural recording is a technique that captures sound in a way that mimics the human ear’s perception, enabling listeners to experience audio as if they were physically present in the environment. This method employs two microphones placed at ear distance, often within a mannequin head or custom-designed dummy head, to replicate the head-related transfer function (HRTF). The result is a 3D audio effect that is particularly effective when listened to through headphones.
The benefits of binaural recording include:
- Realism: It provides a heightened sense of realism by accurately portraying how sound arrives at each ear, including the influence of head and ear shape on sound perception.
- Spatial Awareness: It allows the listener to detect the direction and distance of sounds, enhancing the sense of immersion.
- Emotional Engagement: The lifelike experience can evoke stronger emotional responses, making it ideal for storytelling and media.
Binaural audio is widely used in various fields, including virtual reality, gaming, and ASMR content, where the goal is to create an engaging and enveloping auditory experience.
Ambisonics
Ambisonics provides another avenue for creating immersive audio, allowing for a full-sphere surround sound experience. Unlike traditional stereo or surround sound formats, ambisonics captures sound from all directions around a central point, enabling the playback of audio in any spatial configuration.
This technique is characterized by its use of spherical harmonics to represent sound fields, facilitating a rich and adaptable audio environment. Some key features include:
- Flexibility: Ambisonics can be decoded to various speaker configurations, making it versatile for different playback systems.
- Dynamic Range: This method allows for smoother transitions between sounds and better definition of spatial elements, enhancing the overall audio landscape.
- Immersive Storytelling: It supports a more dynamic narrative flow in audio experiences, making it suitable for immersive installations and gaming.
Ambisonics is particularly beneficial in applications like VR and AR, where a realistic sound environment significantly enhances user experience.
Mixing Techniques for Immersive Formats
Adapting mixing techniques for immersive audio formats involves a shift from traditional stereo mixing to a more spatially aware process. This requires sound engineers to consider the placement and movement of audio elements within a three-dimensional space.
Key adaptations in mixing include:
- 3D Panning: Instead of panning sounds left or right, mixers can position sounds in a 360-degree field, allowing for more intuitive sound placement.
- Depth Control: The use of reverb and delay can help simulate distance, providing a sense of depth that is crucial for immersion.
- Object-Based Mixing: Utilizing object-based audio allows individual elements to be treated as independent sources, providing flexibility in how sounds interact within the space.
By incorporating these techniques, creators can facilitate a fully immersive experience that captures the nuances of sound and elevates the listener’s engagement with the content. The evolution of immersive audio technology continues to push creative boundaries, making it an exciting field for audio production.
Challenges in Implementing Immersive Audio Solutions
The integration of immersive audio solutions into various settings presents a range of challenges that organizations must navigate. These obstacles can stem from technical limitations, user experience barriers, and operational constraints. Addressing these challenges is essential for the successful adoption and implementation of immersive technologies.
Technical Limitations
Immersive audio technologies often face significant technical hurdles that can hinder their effectiveness. These limitations can include hardware constraints, software compatibility issues, and the complexity of audio spatialization.
To understand the technical barriers better, consider the following points:
- Hardware Requirements: High-quality immersive audio systems often require advanced hardware, such as specialized speakers and audio interfaces, which can be costly and difficult to install in existing environments.
- Software Integration: Many immersive audio solutions need to integrate with various software platforms and existing ecosystems, which can lead to compatibility problems and increased development time.
- Audio Spatialization Complexity: Achieving true spatial audio requires sophisticated algorithms and processing power that may not be feasible with standard consumer-grade devices.
User Experience Barriers
User experience plays a critical role in the adoption of immersive audio technologies. Several factors can deter users from fully engaging with these solutions, impacting their overall effectiveness.
The following aspects Artikel the user experience challenges:
- Learning Curve: Users may find immersive audio interfaces complex and challenging to navigate, which could lead to frustration and disengagement.
- Accessibility Issues: Not all users have equal access to the necessary equipment or environments to experience immersive audio, creating a disparity in user experience.
- Perception of Value: Some users may not fully appreciate the benefits of immersive audio over traditional audio formats, which can limit its perceived value and usage.
Potential Solutions and Innovations
Overcoming the challenges associated with immersive audio solutions requires innovative approaches and strategic planning. By addressing technical and user experience barriers, organizations can enhance the adoption of these technologies.
The following strategies could prove beneficial:
- Modular Hardware Design: Developing modular audio systems that can be easily upgraded or customized may help reduce costs and improve accessibility.
- User-Centric Design: Focusing on intuitive user interfaces and providing comprehensive training resources can significantly enhance user engagement and satisfaction.
- Enhanced Marketing of Benefits: Clearly communicating the advantages of immersive audio through case studies and real-life applications can help shift perceptions and increase user interest.
Future Trends in Immersive Audio Development
The landscape of immersive audio is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. As audio experiences become more integral to entertainment, education, and various industries, the development of immersive audio technologies is expected to grow significantly. Key trends on the horizon include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), which will enhance the way audio is created, processed, and experienced.
The convergence of immersive audio with AI and ML is set to transform the auditory experience across many sectors. AI algorithms can analyze sound patterns and user preferences, enabling the customization of audio environments in real-time. This capability allows for individualized soundscapes, where audio can adapt to the listener’s context, preferences, or even emotional state. Machine learning models will likely facilitate advanced spatial audio rendering techniques, creating environments that sound more realistic by mimicking how humans perceive sound in the real world.
Potential Future Applications of Immersive Audio
The implications of immersive audio technology stretch beyond traditional entertainment, with numerous sectors poised to benefit from its applications. The following are key areas where immersive audio is expected to make a significant impact:
- Healthcare: Immersive audio can play a vital role in therapeutic settings. For instance, hospitals might use carefully designed soundscapes to reduce patient anxiety and improve their overall well-being. Virtual reality (VR) environments incorporating immersive audio can assist in pain management and rehabilitation exercises.
- Education: Immersive audio can enhance learning experiences by creating interactive and engaging environments. Students could explore historical events or scientific concepts with audio that adapts to their learning paths, making education more dynamic and impactful.
- Gaming: The gaming industry continues to be at the forefront of immersive audio innovation. Future video games will likely offer players fully immersive sound experiences, allowing them to hear sounds from various directions as if they were part of the game world, thus increasing engagement and realism.
- Live Events: Concerts and events can employ immersive audio to create captivating experiences for audiences. Attendees could enjoy personalized audio experiences tailored to their location within a venue, enhancing the enjoyment of performances.
- Advertising: Brands may utilize immersive audio to create more impactful marketing campaigns. By designing soundscapes that resonate emotionally with consumers, advertisers can cultivate deeper connections and brand loyalty.
The future of immersive audio is not just about enhancing existing experiences; it is about creating entirely new ways for individuals to interact with sound. As technology continues to advance, we can expect more innovative applications that stretch the boundaries of auditory experiences.
The Role of Hardware in Delivering Immersive Audio Experiences
Achieving high-quality immersive audio experiences relies heavily on the hardware utilized in the setup. The right equipment not only enhances the auditory experience but also ensures that the sound is delivered as intended by creators. This section delves into the types of hardware necessary for immersive audio and compares consumer-level options with professional-grade equipment.
The importance of hardware in immersive audio cannot be overstated. Quality audio hardware is essential for capturing, mixing, and reproducing sound accurately. Advanced audio systems allow for multi-dimensional soundscapes that engage listeners more deeply, whether in gaming, virtual reality, or cinematic experiences. To take full advantage of immersive audio formats like Dolby Atmos or DTS:X, specific hardware is required to support the intricate sound placements and movements that characterize these formats.
Essential Equipment for Immersive Audio Setups
To create an effective immersive audio environment, various types of equipment are necessary. The following are key components that contribute to high-quality audio experiences:
- Speakers: Surround sound speakers or specialized immersive audio speakers are essential. These systems often include upward-firing speakers that enhance the vertical dimension of sound.
- Audio Interfaces: High-quality audio interfaces ensure that sound is captured and processed without degradation. They connect microphones and instruments to computers for mixing.
- Headphones: For personal immersive experiences, high-fidelity headphones can deliver spatial audio effects, allowing users to perceive sound from various directions without external noise interference.
- Microphones: Surround microphones or binaural microphones capture sound in a way that mimics human hearing, critical for immersive recording.
- Mixing Consoles: Professional mixing consoles allow for precise control over audio elements, enabling producers to craft an intricate sound environment.
Consumer-level hardware often includes basic home theater systems, soundbars, or gaming headsets that offer surround sound features but may lack the precision and depth of professional-grade setups. In contrast, professional-grade equipment is designed with superior components and technology, ensuring enhanced sound fidelity and the ability to handle complex audio formats. For example, while a consumer soundbar can simulate surround sound, a full surround sound system with dedicated speakers provides a true immersive experience. High-end audio interfaces and mixing consoles also offer features like higher bit rates and sample rates, which are essential for professional audio production.
In summary, the hardware used in immersive audio experiences plays a pivotal role in delivering high-quality sound that transports listeners into another world, whether they are enjoying a film, playing a video game, or experiencing a concert.
User Experience and Immersive Audio
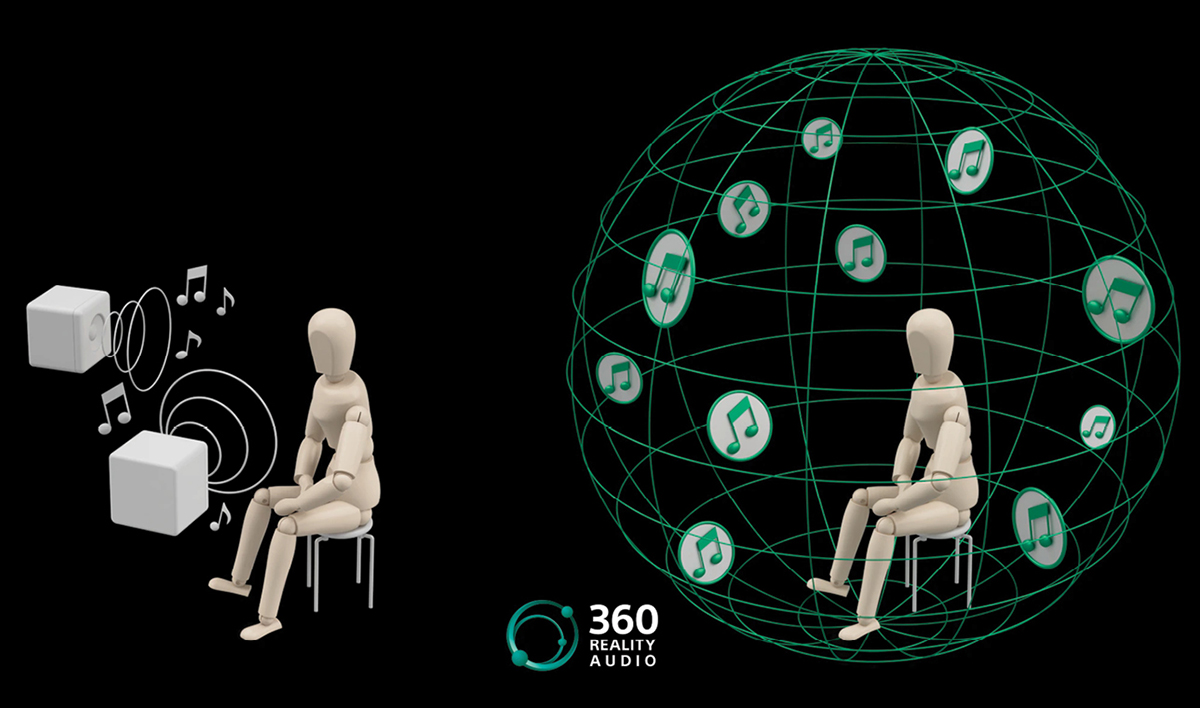
The advent of immersive audio has marked a significant evolution in user experience across various digital platforms. Unlike traditional audio experiences, which often deliver sound in a flat, two-dimensional manner, immersive audio creates a three-dimensional auditory landscape that enhances engagement and emotional connection. As consumers seek more enriching interactions with content, the shift towards immersive audio is not just a trend but a paradigm shift in how users perceive and interact with sound.
Immersive audio reshapes user experience by offering a more realistic and engaging auditory environment. This technology employs techniques like binaural recording and spatial audio to replicate how humans naturally perceive sound from multiple directions. As a result, users can experience content in a manner that feels more like real life. For instance, in gaming, players are able to discern the direction of footsteps or the sound of rustling leaves, leading to a heightened sense of presence and involvement. In the realm of virtual reality (VR), immersive audio is critical; it deepens the user’s sense of place, making experiences more believable and compelling.
User Feedback and Data on Audio Experiences
User feedback has been overwhelmingly positive regarding the transition from traditional to immersive audio experiences. Surveys indicate that approximately 75% of users prefer immersive audio when engaging with content, citing improved realism and emotional impact as primary reasons. This preference is reflected in data collected from various platforms. For instance, a study by Dolby Laboratories revealed that users engaging with immersive audio reported a 50% increase in satisfaction levels compared to standard audio formats.
Additionally, immersive audio has been shown to increase users’ retention rates significantly. In educational platforms using immersive soundscapes, students demonstrated a 30% higher retention rate of information. Testimonials from users highlight that the enhanced audio quality allows them to feel more involved, with many stating that it feels as if they are part of the story rather than mere observers.
User Interfaces Evolution for Immersive Audio Technologies
As immersive audio technology continues to grow, user interfaces must evolve accordingly to provide seamless interactions. Traditional audio players and applications lack the necessary features to fully leverage immersive audio capabilities. New interfaces need to incorporate spatial audio controls, allowing users to manipulate sound sources and customize their auditory experiences. This could include features like sound positioning sliders or immersive environments where users can select how they want to experience sound.
Furthermore, the integration of voice control and adaptive sound settings will play an essential role in the evolution of user interfaces. These functionalities can enhance accessibility, ensuring that users with varying abilities can experience the richness of immersive audio. As more content creators adopt immersive sound technologies, the demand for intuitive, user-friendly interfaces that accommodate these advancements will drive innovation in design and functionality, ultimately leading to a more inclusive and engaging user experience.
Closure
![The Science Behind Immersive Audio – rAVe [PUBS] The Science Behind Immersive Audio – rAVe [PUBS]](https://audiolifeinc.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/immersive-audio-fc5b9d79f5-overlay.png)
In conclusion, immersive audio has revolutionized how we interact with sound across various industries, enhancing user experiences in ways we never thought possible. As we look to the future, the integration of innovative technologies like artificial intelligence will likely further elevate this experience, pushing the boundaries of what we can achieve with sound. This ongoing evolution promises to keep us captivated, making immersive audio an essential part of our daily lives.
FAQ Compilation
What is immersive audio?
Immersive audio refers to sound technologies that create a three-dimensional auditory experience, allowing listeners to perceive sound as coming from all around them rather than just from two speakers.
How does spatial awareness play a role in immersive audio?
Spatial awareness is crucial in immersive audio as it influences how sound is localized and perceived, enhancing the overall experience by making it feel more realistic and engaging.
Is immersive audio only used in entertainment?
No, immersive audio is utilized across various industries, including healthcare for therapy, education for training simulations, and even in virtual reality environments.
What are binaural recordings?
Binaural recordings are audio recordings made using two microphones to create a 3D stereo sound sensation for the listener, resembling how humans naturally perceive sound.
What challenges does immersive audio face?
Challenges include technical limitations in hardware, user experience barriers, and the need for more advanced mixing techniques to create high-quality immersive content.

